How Autophagy Works
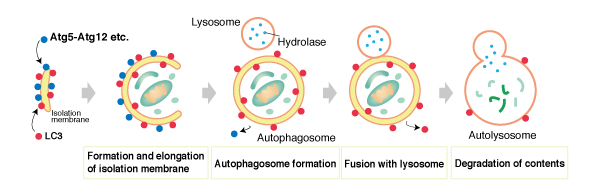
Autophagy is a natural process of self-cleansing and regeneration that takes place in the body. It helps the body to break down waste, old cells, and damaged proteins, ultimately allowing for the healthy production of new cells, proteins, and other vital components necessary for all bodily functions.
The process of autophagy can be broken down into three main parts: initiation, execution, and termination.
Initiation begins with the recognition of material within a cell that needs to be removed by autophagy. Special enzymes are then produced which mark this material for destruction.
During Execution, lysosomes (organelles shaped like bubbles) fuse with these marked materials in order to create double-membrane structures called autophagosomes which make up the actual "autophagic bags". These bags are then filled up with additional things needed to be broken down such as organelles or debris.
Termination involves the breakdown of these contents by enzymes found in lysosomes prior to their release out of the cell as either energy or building blocks for new molecules. This is a continuous cycle that takes place until no more materials need destruction or have been determined beyond repairable capacities.
Autophagy has a multitude of benefits including helping inhibit diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's, promoting longevity through getting rid of potentially harmful compounds which could shorten lifespan, controlling inflammation, and many others. In essence, it keeps our bodies functioning properly by removing any unwanted materials from ourselves so we can keep performing optimally!
ESCRT machinery
ESCRT mediates membrane fission and prevents glycosylation of lysosomal membrane proteins on IAM. Failure to generate OAM limits access to lysosomal lipases and proteases and impairs degradation. These findings indicate that ESCRT plays a critical role in autophagy.
mTORC1 complex
The mTORC1 complex is an essential regulator of anabolic processes and autophagy. It phosphorylates downstream effectors, including the ribosomal protein S6 kinase and the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-BP. When mTORC1 is inactive, autophagy is inhibited. Alternatively, inhibition of mTORC1 stimulates the formation of the pro-autophagic complex and the production of autophagosomes.
TORC1
TORC1 regulates microautophagy through phosphorylation of the protein Vps27. However, it does not modulate the flux through the MVB pathway. Instead, it targets Vps27 to endosomal membranes, which are rich in phosphatidyl 3-phosphate.
RAB7
Autophagy is an important process in our bodies, and RAB7 plays a crucial role in the process. This enzyme controls autophagosome formation and transport. It is also involved in the elongation of isolation membranes during mitophagy. Rab7 may also mediate the fusion between elongating autophagosomes and lysosomes. Ultimately, autophagy leads to the sequestration of pathogenic bacteria.
Phosphorylated UVRAG
Phosphorylated UVRAG inhibiting autophagy is caused by the phosphorylation of UVRAG on mTORC1. The mTOR pathway controls the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes during starvation, a process that is essential for maintaining cell viability. The phosphorylation of UVRAG on the mTOR pathway enhances UVRAG's association with the RUBICON protein complex, which is necessary for autophagosome maturation. UVRAG also interacts with the HOPS complex, a regulatory factor for autophagosome maturation.
Class III PI 3-kinase VPS34
Autophagy is a process in which cells recycle proteins by undergoing biogenesis and remodeling of intracellular membranes. Autophagosome membrane assembly can be triggered from a variety of sources. For example, the autophagosome membrane can be generated from the ER, Golgi, plasma membrane, or mitochondria. Generally, the ER membrane is the initial source. When nutrients are unavailable, Atg proteins localize to the ER membrane.
PI3P
Autophagy is an important pathway that regulates cellular energy metabolism and self-renewal. It also plays a key role in biological development and homeostasis. In tumor therapy, autophagy can play a dual role by suppressing tumor cells and promoting cell death. Autophagy is also a potent tumor suppressor, limiting the number of tumor cells and reducing the risk of DNA mutation. However, there are many unknowns associated with autophagy. Researchers are still trying to unravel its origin, signal transduction pathways, and effects on cell survival.
RAB7-mediated autophagy
Autophagy is an important process involved in cell growth, survival, development, and cell death. Its impairment is linked to numerous pathophysiological processes in humans, including neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disorders, and myopathy. This regulated process has important implications for the development of novel therapeutics.
ESCRT-mediated autophagy
The ESCRT protein is involved in a number of autophagy processes in cells, including microautophagy and macroautophagy. Its complex with accessory proteins induces membrane budding away from the cytoplasm, which is a unique mode of membrane remodeling. It is comprised of five proteins, including Vps4, a type I AAA+ ATPase with 430 amino acids.
TORC1-mediated autophagy
To understand the mechanism of TORC1-mediated autophagy, it is important to know the functions of the TORC1 protein. TORC1 has multiple roles in the nervous system, including regulating lipid metabolism and regulating brain size. It has also been implicated in rat brain morphology, including reduced soma and dendritic arbours, and increased dendritic spines. Further, this protein is involved in the formation of autophagosomes and degradation of autophagic cargo.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to do Intermittent Fasting for Beginners?
Getting started with intermittent fasting can seem daunting. But understanding how intermittent fasting works can make it easier to begin.
First, decide which type of fasting you'd like to do. There are three main types, time-restricted intermittent fasting, the 16/8 and the 5/2. Time-restricted eating means that you eat only during certain hours of the day. The 16/8 method, on the other hand, requires that you eat within an 8-hour time frame and then skip the meals for the remainder of the day. The 5 to 2 diet includes two days of calorie restriction per week with normal eating on the rest.
Stock up on healthy foods that you can make quickly and eat whenever hunger strikes. These include nutrient-rich protein such as eggs, beans, and legumes; healthy fats like nuts and seeds or oil; high-fibre carbohydrate like quinoa and buckwheat; and a variety of fresh fruits and veggies to ensure you get your daily doses of vitamins and minerals.
Planning your meals is just the beginning. You need to plan how you'll handle social pressures when dining out with loved ones or friends. It's important to have self-control when you live an intermittent fast life. Flexibility is important when staying focused on your goals. So, try to include sweet spot meals that give you more satisfaction but don't overcomplicate the work done in the previous weeks and months.
To maintain motivation, it is important to keep track of results.
Intermittent fasting is a way to lose belly weight.
Questioning the status quo is key to finding solutions. Traditional wisdom suggests that exercise and caloric reduction are the best ways to lose belly fat. However, recent research has revealed that intermittent fasting is more effective and faster than previously believed.
Intermittent fasting is when you eat food in a specific 8-12 hour window per day and fast for 12-16 hours between meals. These fasting periods don't require you to count calories or portion control as much as with calorie restriction.
When practiced correctly, intermittent fasting can ramp up metabolism and burn stored fats more efficiently than other methods of long-term weight loss. It can also improve mental clarity and digestion, lower inflammation, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such type 2 diabetes.
Plus, the practice requires little effort from the user -- just set a timer for when you eat and then stay away from food until the timer goes off again! Intermittent fasting offers a straightforward way to lose belly fat and improve health outcomes.
Intermittent fasting can help to accelerate your weight loss journey. You still need to ensure you're eating healthy and nutritious foods during your eating windows and getting enough exercise. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding or have any other medical conditions, it is a good idea consult your doctor before trying a new diet.
What is permitted and prohibited during intermittent fasting
Understanding the rules of intermittent fasting is imperative to achieving desired results. It's not just about eating less but ensuring that you're consuming the right types and amounts of food during specific periods.
Intermittent Fasting refers to times when you will only eat food, and other times when you must eat fewer calories. These "fasting windows" can last anywhere from 16 to 24 hrs, giving your body plenty of time to digest and cleanse difficult-to-digestible foods, as well as to speed up your metabolism.
But, you don't need to fast. These are good times to enjoy nutrient rich beverages like tea, lemonwater, or water. Also, you can enjoy calorie-free snacks like vegetables and fruits. However, they must be consumed with no added fat or oil.
This isn't an excuse for a free-for-all on high-calorie foods and sugary treats when you come out of your fast either - it does pay to maintain healthy eating habits overall. After the recommended number of hours you have been fasted, you can start to add unhealthy foods like chips and other unhealthy options. These will quickly undo all the hard work. Consume low glycemic food during your meal windows to avoid nutrient-dense foods like whole grains and lean protein.
Intermittent fasting is not a one-size fits all approach. Everybody is unique and will react differently to the same diet. Consult a doctor or nutritionist before you embark on any new diet plan. This is especially important if there are any existing health conditions. Also, make sure you get enough sleep and keep hydrated during the whole process.
What research says about intermittent fasting and weight loss?
You may be surprised at the possibilities of intermittent fasting and weight reduction. Research suggests that changing your eating habits throughout the day can help with weight management and overall health. Research has also shown that structured fasting can boost metabolism, reduce food cravings as well as promote fat burning.
Intermittent Fasting is a fascinating concept that relies on several physiological processes. It can be used to increase health and weight loss. Recent studies have shown that intermittent fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, cell repair and hormone balance, as well a positive effect on bacterial populations.
Collectively, these adjustments offer promise for people seeking a lifestyle change or an additional tool in their weight-loss arsenal. People seeking to manage long-term goals will benefit from increased energy and mental clarity.
The evidence supporting positive hormone balance through fasting protocols is equally impressive. This prevents you from feeling deprived or too satisfied by indulgences. This allows for optimal caloric intake while maintaining physical activity program goals.
It is easy to create a trusted plan of action that works by leveraging the scientific evidence and conclusions regarding intermittent fasting and its effect on sustained well-being goals.
What foods are you unable to eat while intermittent fasting?
When it comes to intermittent fasting, abstinence is key. To stick to your plan, you will need to eliminate certain food groups.
You can make a big difference in the success of your fasts by avoiding processed foods and sugary goods. No matter how difficult it is, avoid sugary cereals, candy bars and ice cream.
Also, it is best to avoid saturated fats. To avoid any health hazards associated with prolonged fasting, foods such as fried foods and fatty meats should be avoided. Any food items containing refined carbohydrates, like white bread or chips, should also be avoided while fasting.
Alcohol should be avoided during fasting. It contains lots of empty calories, which can hinder weight loss. You'll be able to keep your fasts on track if you stick to the above guidelines.
Statistics
- When diet composition was controlled, most protocols were consistent with Health Canada and American Heart Association guidelines: 55% carbohydrates, 20% fat, and 25% protein. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The rigor of fasting also varied, with several studies allowing 25% of regular caloric consumption during fasting periods. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Fat consumption was examined in 1 study, which compared dietary fat intake of 45% versus 25% at the expense of carbohydrate intake. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- In 2018, 63.1% of Canadian adults were overweight or obese. (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
External Links
jamanetwork.com
sciencedirect.com
- Influence of short-term repeated fasting on the longevity of female (NZBxNZW)F1 mice - ScienceDirect
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- The MATADOR study - PubMed - Intermittent energy restriction increases weight loss efficiency in obese men
- INTERMITTENT FEASTING AND HUMAN METABOLIC HEALTH- PMC
annualreviews.org
How To
Tips and tricks for adhering to an intermittent fasting schedule
Intermittent Fasting is a popular way to lose weight and improve your health. It involves eating alternatingly and abstaining entirely from food. While intermittent fasting can improve your health and help you reach your goals, sticking to a consistent schedule can be challenging. Here are some tricks and tips to help ensure you stay on track.
-
Find a routine that works for you: Everyone is different, so it's important to find one that works for you. Some people prefer eating earlier in the evening and going fast the next day. Other people prefer eating later in the afternoon and going fast the next morning. Test different ways to find out what works for each of you.
-
Keep healthy snacks handy: It is important to stay nourished while you fast, especially if it's for a prolonged period. Healthy snacks like nuts, seeds and fruit are a great way to keep your energy up and your hunger at bay.
-
Plan: Planning can help make sticking to your intermittent fasting schedule easier. To help you stay on track, prepare your meals ahead of time or pack healthy snacks for work and other activities.
-
Hydration is key: Water can keep you hydrated and full while fasting. Drink at least 8-10 cups water per day. You might also consider drinking unsweetened or herbal coffee, which are low-calorie and hydrating.
-
Flexibility is a virtue: You can be flexible with your intermittent fasting program. Life happens and you might need to change your routine from time to time. Do not beat yourself up if things go wrong.
It can be difficult to adhere to an intermittent fasting program without practice and dedication. With the right mindset, and some helpful strategies, you can make it a part of your healthy lifestyle. With some trial-and-error, you will find a routine you like and that helps you reach your health and fitness goals.
Did you miss our previous article...
https://paleovsketo.com/intermittent-fasting/constipation-food-that-helps-relieve-constipation






